Si utilizas un diseño basado en View, hay tres opciones principales para
con la implementación de botones de activación. Te recomendamos que utilices
Componente SwitchMaterial
de la página de Material
Biblioteca de componentes:
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:padding="16dp">
<com.google.android.material.switchmaterial.SwitchMaterial
android:id="@+id/material_switch"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/material_switch"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
Es posible que las apps heredadas aún usen la versión anterior
SwitchCompat AppCompat
como se muestra en el siguiente ejemplo:
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:padding="16dp">
<androidx.appcompat.widget.SwitchCompat
android:id="@+id/switchcompat"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/switchcompat"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
En el siguiente ejemplo, se muestra
AppCompatToggleButton:
que es otro componente heredado que tiene una IU notablemente diferente:
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:padding="16dp">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/toggle_button_label"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf="@id/toggle"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_chainStyle="packed"
app:layout_constraintBaseline_toBaselineOf="@id/toggle"
android:text="@string/toggle_button" />
<androidx.appcompat.widget.AppCompatToggleButton
android:id="@+id/toggle"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@id/toggle_button_label"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"/>
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
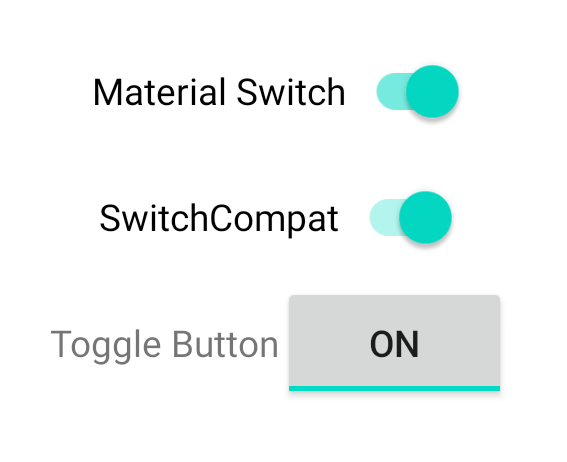
Estos tres componentes ofrecen el mismo comportamiento, pero se ven diferentes. El
Las diferencias entre SwitchMaterial y SwitchCompat son sutiles, pero
AppCompatToggleButton se ve muy diferente:
Cómo controlar los cambios de estado
SwitchMaterial, SwitchCompat y AppCompatToggleButton son subclases
de CompoundButton, que
le brinda un mecanismo común para manejar los cambios de estado verificados. Implementas
una instancia de
CompoundButton.OnCheckedChangeListener
y agregarla al botón, como se muestra en el siguiente ejemplo:
Kotlin
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
val binding: SwitchLayoutBinding = SwitchLayoutBinding.inflate(layoutInflater)
setContentView(binding.root)
binding.materialSwitch.setOnCheckedChangeListener { _, isChecked ->
if (isChecked) {
// The switch is checked.
} else {
// The switch isn't checked.
}
}
}
}
Java
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
SwitchLayoutBinding binding = SwitchLayoutBinding.inflate(getLayoutInflater());
setContentView(binding.getRoot());
binding.materialSwitch.setOnCheckedChangeListener((buttonView, isChecked) -> {
if (isChecked) {
// The switch is checked.
} else {
// The switch isn't checked.
}
});
}
}
CompoundButton.OnCheckedChangeListener es una interfaz de método abstracto único
(o interfaz SAM), por lo que puedes implementarlo como lambda. La lambda se llama
cada vez que cambie el estado activado y el valor del valor booleano isChecked
que se pasa a la expresión lambda indica el nuevo estado verificado.


