WindowInsetsCompat を使用すると、
アプリは、画面キーボード(別名:
IME など)は、
システムバーとどのように相互作用するかを示します。アプリでは
WindowInsetsAnimationCompat
ソフトウェア キーボードを閉じたり開いたりしたときにシームレスに遷移するようにします。
前提条件
ソフトウェア キーボードの制御とアニメーションを設定する前に、 エッジ ツー エッジで表示できます。これにより、 次のようなシステム ウィンドウ インセットを処理します。 システムバーと画面キーボードです。
キーボード ソフトウェアの表示を確認する
WindowInsets を使用してソフトウェアを確認する
キーボードの表示設定。
Kotlin
val insets = ViewCompat.getRootWindowInsets(view) ?: return val imeVisible = insets.isVisible(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.ime()) val imeHeight = insets.getInsets(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.ime()).bottom
Java
WindowInsetsCompat insets = ViewCompat.getRootWindowInsets(view); boolean imeVisible = insets.isVisible(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.ime()); int imeHeight = insets.getInsets(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.ime()).bottom;
別の方法として、
ViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener
ソフトウェア キーボードの表示の変化をモニタリングできます。
Kotlin
ViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener(view) { _, insets ->
val imeVisible = insets.isVisible(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.ime())
val imeHeight = insets.getInsets(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.ime()).bottom
insets
}
Java
ViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener(view, (v, insets) -> {
boolean imeVisible = insets.isVisible(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.ime());
int imeHeight = insets.getInsets(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.ime()).bottom;
return insets;
});
アニメーションをソフトウェア キーボードと同期させる
ユーザーがテキスト入力フィールドをタップすると、キーボードが所定の位置にスライドして 画面下部に表示されます。
<ph type="x-smartling-placeholder">「Unsynchronized」というラベルの例にはデフォルトの動作を、図 2 に示します。 Android 10(API レベル 29)では、アプリのテキスト フィールドとコンテンツが キーボードの音と連動する代わりに、 不快な印象を与える可能性がある動作。
Android 11(API レベル 30)以降では、
WindowInsetsAnimationCompat: アプリの遷移を 画面下からキーボードを上下にスライドさせる外観 「Synchronized」というラベルの例のように、図 2 に示します。
構成
WindowInsetsAnimationCompat.Callback
キーボードのアニメーションと同期するようにします。
Kotlin
ViewCompat.setWindowInsetsAnimationCallback(
view,
object : WindowInsetsAnimationCompat.Callback(DISPATCH_MODE_STOP) {
// Override methods.
}
)
Java
ViewCompat.setWindowInsetsAnimationCallback(
view,
new WindowInsetsAnimationCompat.Callback(
WindowInsetsAnimationCompat.Callback.DISPATCH_MODE_STOP
) {
// Override methods.
});
WindowInsetsAnimationCompat.Callback にはオーバーライドするメソッドがいくつかありますが、
つまり
onPrepare(),
onStart(),
onProgress(),
および
onEnd()
まず、レイアウトが変更される前に onPrepare() を呼び出します。
onPrepare は、インセット アニメーションの開始時とビューの開始時に呼び出されます
アニメーションにより再レイアウトできますこれを使用して開始状態を保存し、
これはビューの底辺の座標です

onPrepare() の使用:
開始状態を記録します。
次のスニペットは、onPrepare の呼び出し例を示しています。
Kotlin
var startBottom = 0f
override fun onPrepare(
animation: WindowInsetsAnimationCompat
) {
startBottom = view.bottom.toFloat()
}
Java
float startBottom;
@Override
public void onPrepare(
@NonNull WindowInsetsAnimationCompat animation
) {
startBottom = view.getBottom();
}
onStart は、インセット アニメーションが開始されると呼び出されます。これを使用して、
ビュー プロパティをレイアウト変更の最終状態にします。すでに
OnApplyWindowInsetsListener コールバックがビューのいずれかに設定されているため、すでに
呼び出されることになります。ここで、ビューの最終状態を保存することをおすすめします。
プロパティです。
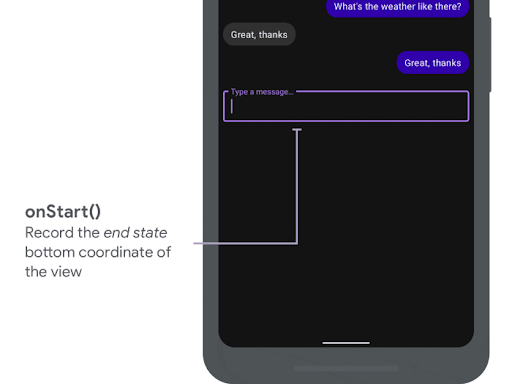
onStart() を使用した録画
作成します。
次のスニペットは、onStart の呼び出し例を示しています。
Kotlin
var endBottom = 0f
override fun onStart(
animation: WindowInsetsAnimationCompat,
bounds: WindowInsetsAnimationCompat.BoundsCompat
): WindowInsetsAnimationCompat.BoundsCompat {
// Record the position of the view after the IME transition.
endBottom = view.bottom.toFloat()
return bounds
}
Java
float endBottom;
@NonNull
@Override
public WindowInsetsAnimationCompat.BoundsCompat onStart(
@NonNull WindowInsetsAnimationCompat animation,
@NonNull WindowInsetsAnimationCompat.BoundsCompat bounds
) {
endBottom = view.getBottom();
return bounds;
}
アニメーションの実行中にインセットが変更されると、onProgress が呼び出されます。
キーボード入力中にすべてのフレームで通知を受け取れるようにします。
作成します。ビューがアニメーションになるようにビュー プロパティを更新する
キーボードとの同期を行えます。
この時点で、レイアウトの変更はすべて完了しています。たとえば
View.translationY: ビューを移動します。この値は、使用するたびに
最終的に 0 に到着して元のレイアウト位置に到達します。
onProgress() の使用:
アニメーションを同期します。
次のスニペットは、onProgress の呼び出し例を示しています。
Kotlin
override fun onProgress(
insets: WindowInsetsCompat,
runningAnimations: MutableList<WindowInsetsAnimationCompat>
): WindowInsetsCompat {
// Find an IME animation.
val imeAnimation = runningAnimations.find {
it.typeMask and WindowInsetsCompat.Type.ime() != 0
} ?: return insets
// Offset the view based on the interpolated fraction of the IME animation.
view.translationY =
(startBottom - endBottom) * (1 - imeAnimation.interpolatedFraction)
return insets
}
Java
@NonNull
@Override
public WindowInsetsCompat onProgress(
@NonNull WindowInsetsCompat insets,
@NonNull List<WindowInsetsAnimationCompat> runningAnimations
) {
// Find an IME animation.
WindowInsetsAnimationCompat imeAnimation = null;
for (WindowInsetsAnimationCompat animation : runningAnimations) {
if ((animation.getTypeMask() & WindowInsetsCompat.Type.ime()) != 0) {
imeAnimation = animation;
break;
}
}
if (imeAnimation != null) {
// Offset the view based on the interpolated fraction of the IME animation.
view.setTranslationY((startBottom - endBottom)
* (1 - imeAnimation.getInterpolatedFraction()));
}
return insets;
}
必要に応じて、onEnd をオーバーライドできます。このメソッドは、アニメーションの後で呼び出されます。
終了です。ここで一時的な変更をクリーンアップします。
参考情報
- WindowInsetsAnimation ご覧ください。

