Sorry, Ozempic users.
Bariatric surgery leads to more weight loss that lasts longer, compared to drugs like Ozempic and Wegovy and behavioral changes such as diet and exercise, new research finds.
“Metabolic and bariatric surgery remains the most effective and durable treatment for severe obesity. Unfortunately, it also remains among the most underutilized,” said study co-author and bariatric surgeon Dr. Marina Kurian of NYU Langone Health.
Researchers reviewed data from approximately 20,000 weight-loss patients who participated in clinical studies and trials in the last few years.
They found that obesity drugs and weight-loss surgery proved far superior to diet and exercise, which resulted in an average weight loss of 7.4% — those pounds were typically regained within four years.
Five months of weekly injections of semaglutide — the active ingredient in Ozempic and Wegovy — led to a weight loss of 10.6%. These drugs mimic GLP-1 — the hormone the body naturally produces after eating — to make people feel full, reducing their cravings.
Nine months of tirzepatide — sold under the brand names Mounjaro and Zepbound — produced weight loss of 21.1%.
But the researchers found that once these treatments stopped, within a year, patients regained about half the weight they had lost.
Tirzepatide patients who continued with the injections tended to plateau at 17 to 18 months with 22.5% of their weight lost. Patients on semaglutide hit a roadblock at 14.9% weight loss during the same period.
Two popular surgical procedures, meanwhile, produced a weight loss around 30% one year after the operation. Patients maintained a 25% weight loss up to 10 years after surgery, the researchers found.
“Surgery needs to play a bigger role in obesity treatment and be considered earlier in the disease process,” Kurian added. “It is no longer a treatment of last resort and should not be withheld until more severe disease develops. There is no medical reason for this.”
The research was presented Tuesday at the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting.
The society reports that nearly 280,000 weight-loss procedures were performed in the US in 2022, representing only about 1% of those who are eligible for them based on their weight and height.
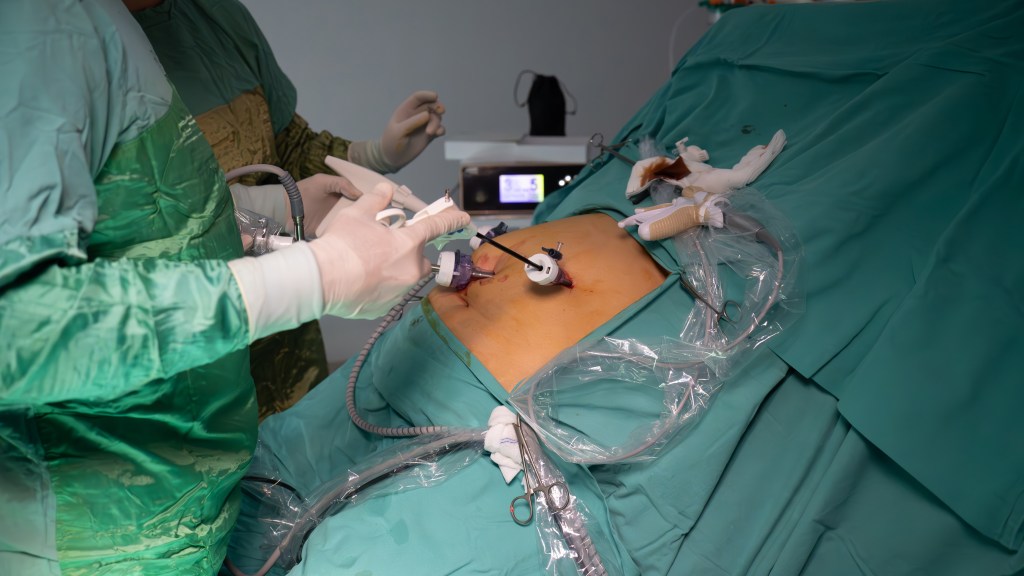
Gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy are two types of weight-loss surgeries that reduce the size of the stomach. Some people may be hesitant to opt for surgery because recovery can take weeks.
There are potential drawbacks to obesity meds as well, including various unpleasant side effects. In a July 2023 survey, 4% of adults admitted to taking a prescription drug to lose weight.
All the while, obesity rates continue to rise, affecting more than 42% of Americans, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The serious condition has been shown to weaken the body’s immune system, cause chronic inflammation and increase the risk of cardiovascular disease, stroke, Type 2 diabetes and certain cancers.
A recent study warned that uncontrolled high blood pressure, diabetes and obesity will lead to at least six in 10 US adults being diagnosed with cardiovascular disease within the next 30 years.